It's no wonder that so many of the Next Big Things in pharmacology end up, a few years later, being implicated in causing disease and even death.
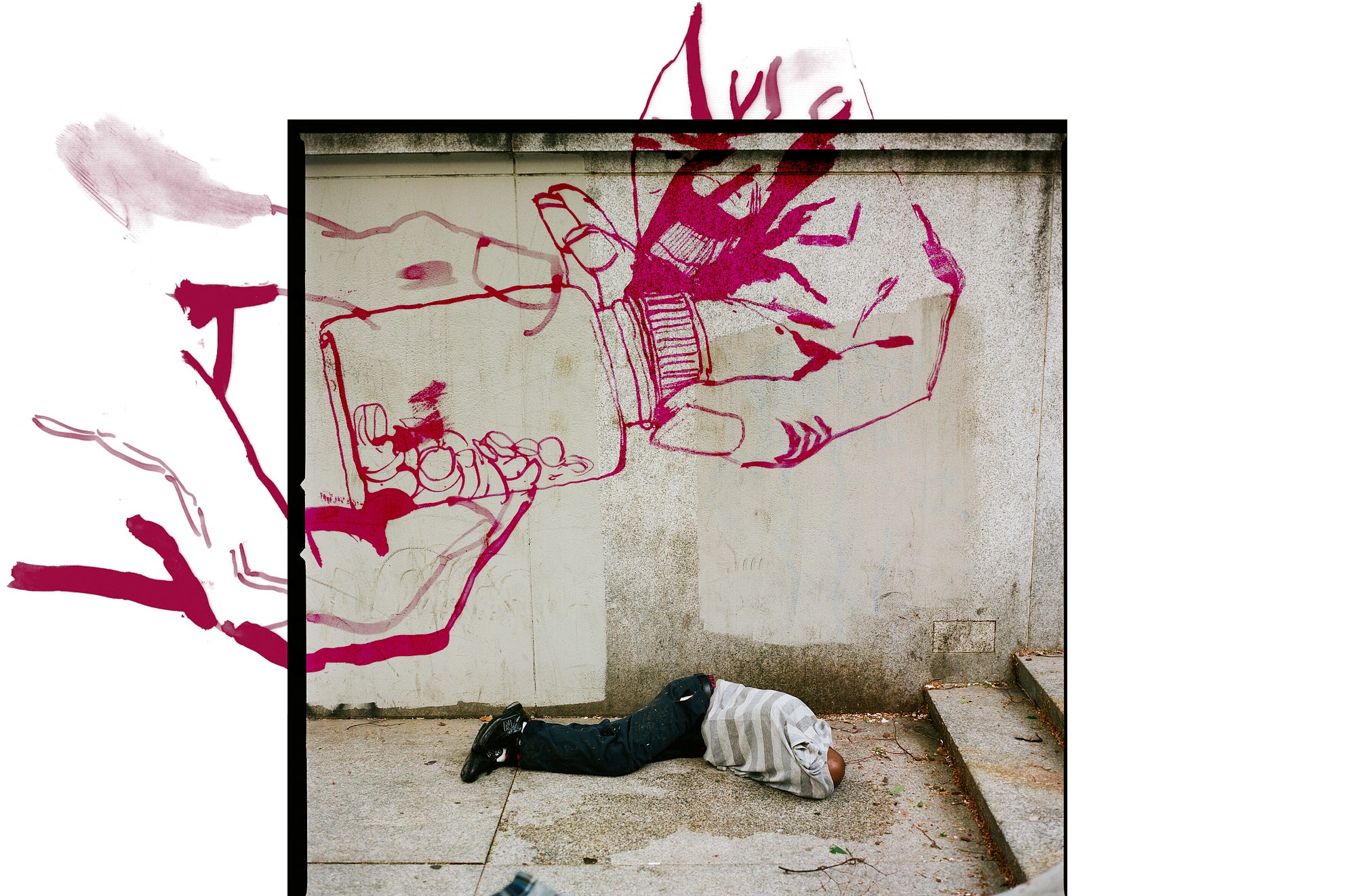
The Best-Selling, Billion-Dollar Pills Tested on Homeless People
How the destitute and the mentally ill are being used as human lab rat
By Carl Elliott
Photographs by Jeffrey StockbridgeIllustrations by Matt Rota
Two years ago, on a gray January afternoon, I visited the Ridge Avenue homeless shelter in Philadelphia. I was looking for poor people who had been paid to test experimental drugs. The streets outside the shelter were lined with ruined buildings and razor wire, and a pit bull barked behind a chain-link fence. A young guy was slumped on the curb, glassy-eyed and shaky. My guide, a local mental health activist named Connie Schuster, asked the guy if he was okay, but he didn’t answer. “My guess is heroin,” she said.
We arrived at the shelter, where a security guard was patting down residents for weapons. It didn’t take long for the shelter employees to confirm that some of the people living there were taking part in research studies. They said that the studies are advertised in local newspapers, and that recruiters visit the shelter. “They’ll give you a sheet this big filled with pills,” a resident in the shelter’s day room told me the next day, holding up a large notebook. He had volunteered for two studies. He pointed out a stack of business cards on a desk next to us; they had been left by a local study recruiter. As we spoke, I noticed that an ad for a study of a new ADHD drug was running on a television across the room.
If you’re looking for poor people who have been paid to test experimental drugs, Philadelphia is a good place to start. The city is home to five medical schools, and pharmaceutical and drug-testing companies line a corridor that stretches northeast into New Jersey. It also has one of the most visible homeless populations in the country. In Philly, homeless people seem to be everywhere: sleeping in Love Park, slumped on benches in Suburban Station, or gathered along the Benjamin Franklin Parkway, waiting for the free meals that a local church gives out on Saturdays.
* * * * *
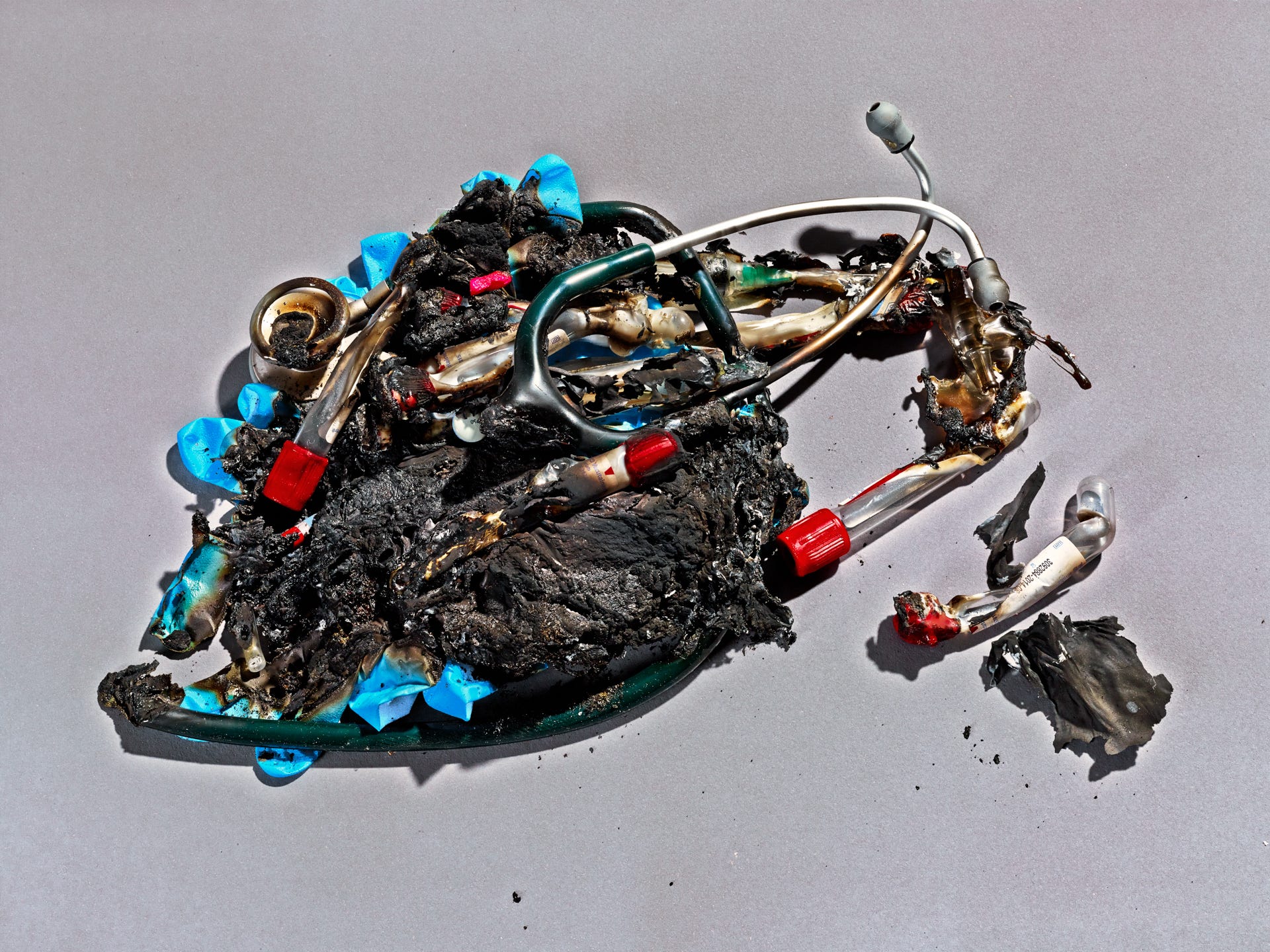
Read the whole article.Why Are Dope-Addicted, Disgraced Doctors Running Our Drug Trials?
By Peter Aldhous
Photographs by Grant Cornett
At around 7 p.m. on February 28, 2003, a 66-year-old woman showed up at the Pioneers Memorial Hospital in Brawley, a small Californian town not far from the Mexican border. She was seen by one of the doctors on duty in the emergency room that night, a man named Michael Berger. He learned that the woman, identified as “B.P.” in a later investigation, was in pain. A cramping sensation in her right thigh was radiating down her calf. Records show that she had a weak pulse in the same leg, and was short of breath. Her right foot felt numb.
Berger had options. He might have reviewed B.P.’s medical records, or tried to reach her primary care doctor to learn more about her history. He might have ordered an ultrasound or an x-ray. Either scan could have revealed the blockage in the artery in B.P.’s right leg. But Berger didn’t do those things. After consulting with a colleague, he sent B.P. home, with instructions to rest, drink plenty of fluids and take painkillers and blood-thinning meds. When she returned to the ER two days later, her leg was pale and cold—too far gone to save. She was flown to a larger hospital in San Diego, where surgeons removed the limb above the knee.
Berger’s career did not improve much afterwards. One day in 2004, he turned up for work impaired, a situation he blamed on taking sleeping pills. Other problems were noted when his employers asked a team of doctors to review his performance: failing to properly monitor patients after prescribing them dangerous drugs; prescribing excessive amounts of painkillers to his wife; a series of incidents while driving, which may have been related to his own drug use.
In 2008, the Medical Board of California put Berger on a seven-year probation. It was an unusually lengthy sanction, and it included limits on his ability to prescribe narcotics, and a requirement that he take regular blood tests to check for drug abuse. By then his career as an ER physician was effectively over: The California Emergency Physicians Medical Group, which employs ER doctors at Pioneers and dozens of other hospitals across the state, had handed him an indefinite suspension. Already his mid-60s, you might imagine that Berger would have taken these sanctions as a cue to slip into retirement.
But that’s not what happened.


No comments:
Post a Comment